Solar heating systems are classified as “active” or “passive” solar heating systems, or a combination of both. We will first look at active systems.
Active solar heating systems are comprised of collectors, a distribution system, and a storage device.
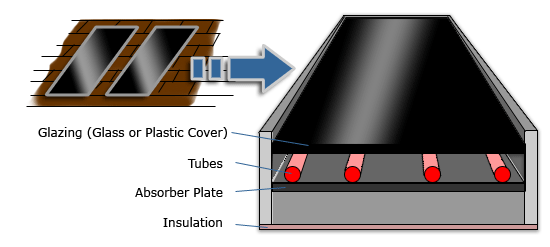
Instructions: Click on the hot spots in the image below to find out more about the main components of an active solar heating system.
Active solar heating systems operate as follows:
- Flat plate collectors are usually placed on the roof or ground in the sunlight. The top or sunny side has a glass or plastic cover to let the solar energy in. The inside space is a black (absorbing) material to maximize the absorption of the solar energy.
- Cold water is drawn from the storage tank by pump #1 and is pumped through the flat plate collector mounted on the roof of the house.
- The water absorbs the solar energy and is returned back to the tank.
- Warm water from the tank is pumped by pump #2 though the heating coil.
- The fan blows air (from the room) over the heated coil, and the heated air then passes into the room and heats the room.
- Cold air sinks to the bottom and is recirculated over the heating coil.
Note: The standby electric coil is automatically turned on and provides the heat when the water temperature to the heating coil drops because of consecutive cloudy days.
Instruction : Click the “play” button to observe the operation of an Active Solar Heating System:
Collector’s Efficiency is the ratio of solar radiation(link is external) that is captured and transferred to the collector or heat transfer fluid.
The efficiency of a collector can be expressed as:
Collector's Efficiency=(Useful energy deliveredIsolation on collector) × 100%
Typical collector efficiencies range from 50–70 percent.