Cost
The most obvious place to start comparing energy sources is cost. We all want electricity to be cheap (and in many states, electric utilities are mandated by law to choose the cheapest fuel available, regardless of environmental impact or any other criteria). Power plants have construction and operational costs, and these are very different for plants that use different types of fuels. A range of illustrative construction costs for power plant technologies is shown in Comparative Construction Costs for Power Plant Technologies, while a range of illustrative operational costs is shown in Comparative Operational Costs for Power Plant Technologies.
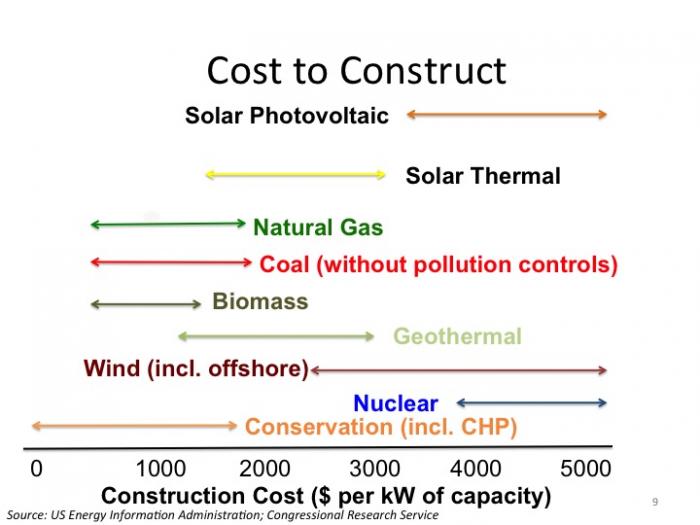
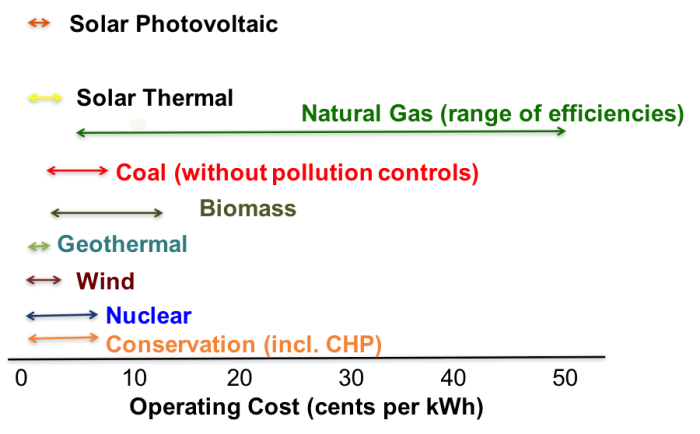
So, which fuel source for power plants is cheapest? Looking at the diagrams above, this is a hard question to answer. Some technologies (like wind, solar and nuclear energy) have high construction cost but low operational cost. Others have low construction costs but higher operational costs (like coal and natural gas). So which is cheaper to build – a natural gas plant or a wind farm?
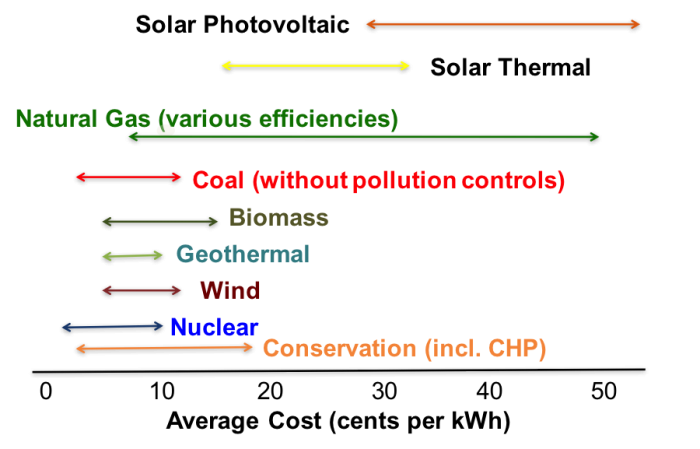
Often times the construction cost and fuel cost are combined to get a single measure of “average” cost per unit of electricity produced. In the electricity business, this is sometimes called a “levelized cost.” These average costs for various power generation technologies are shown in Average Cost of Electricity for Different Technologies. Note that these are pure engineering and fuel costs – they do not include the social costs of any environmental damage associated with electricity production and do not include any explicit subsidies like tax credits.