Global Energy Uses
We are all aware of some of the ways we use energy — heating and cooling our homes, transporting ourselves via car, bus, train, or plane — but there are many other uses of energy that we tend not to think about. For instance, growing food and getting it onto your plate uses energy — think of the farming equipment, the food processing plant, the transportation to your local store. Or, think of manufactured items — to make something like a car requires energy to extract the raw materials from the earth and then assembling them requires a great deal of energy. So, when you consider all of the different uses of energy, we see a dominance of industrial uses:
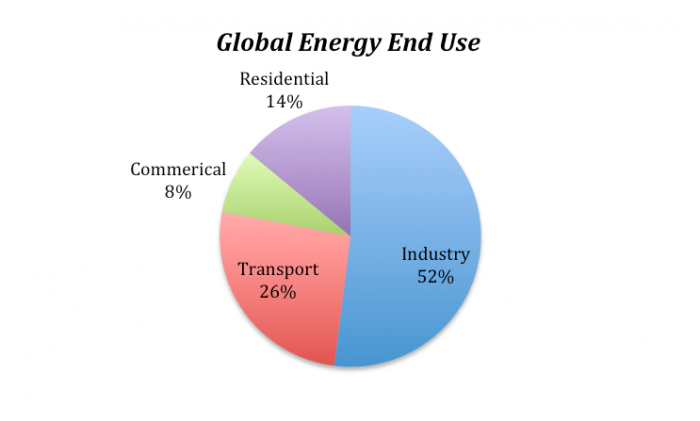
The image is a pie chart titled "Global Energy End Use," showing the distribution of global energy consumption across different sectors. The chart is divided into four segments, each representing a different sector with corresponding percentages:
- Industry: The largest segment, colored in blue, represents 52% of global energy end use.
- Transport: The second largest segment, colored in red, accounts for 26% of the energy consumption.
- Residential: Represented by a purple segment, this sector uses 14% of the global energy.
- Commercial: The smallest segment, colored in green, constitutes 8% of the energy end use.
Each segment is labeled with the sector name and its percentage, providing a clear breakdown of how global energy is utilized across these sectors.
